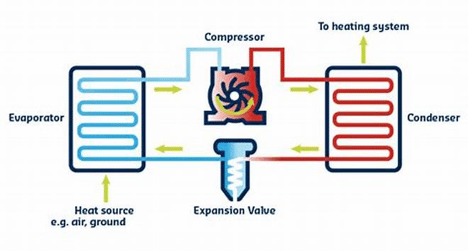
A heat pump is a mechanical-compression cycle refrigeration system for heating or cooling. It is typically more energy-efficient than other systems because it moves heat rather than generates it.
In the winter, a heat pump moves heat from the warm air stored under the ground outside into your home. A heat pump uses a small amount of external power to accomplish the work of transferring energy from the heat source to the heat sink.
Related: How Do I Know if I Have a Heat Pump?
Table Of Contents
- 1 How does a Heat Pump Work?
- 2 Main Components — Heat Pump
- 3 Uses — Heat Pump
- 4 How does a Heat Pump work in the winter
- 5 How does a mini split heat pump work in cold weather?
- 6 Working of Heat Pump — In Summer
- 7 How does a Heat Pump make a House Warm during Winter and Cold during Summer?
- 8 What is the Relation between Heat Pump Efficiency and Temperature?
- 9 Is it safe to turn off the Heat Pump at Night?
- 10 Do Ecobee thermostats work with heat pumps?
- 11 Do Honeywell thermostats work with heat pumps?
- 12 What size heat pump do you need for an average-size home?
- 13 Heat pumps or Central Air conditioners, which one should I choose?
- 14 Conclusion
How does a Heat Pump Work?
The basic principle behind all heat pumps is the same: they move heat rather than generate it. Heat pumps can do this because they rely on the refrigeration cycle.
A heat pump uses a refrigerant to absorb heat from the air and transfer it to the home. The refrigerant is circulated through a series of coils and a compressor. The compressor pumps the refrigerant through the system, and the coils absorb heat from the air. The refrigerant is then condensed and released into the home, releasing heat.
The refrigeration cycle is a process in which heat is transferred from a lower to a higher temperature. The heat pump uses this process to transfer heat from the outside air or ground to the inside of a building. The heat pump can also be reversed to transfer heat from the inside of a building to the outside.
Main Components — Heat Pump
The main components of a heat pump are the compressor, evaporator, and condenser. The compressor pumps refrigerant through the system. The evaporator absorbs heat from the air, and the condenser releases heat into the air.
A heat pump consists of four main components:
- Evaporator (Indoor Unit)
- Condenser (Outdoor Unit)
- Compressor
- Metering device
The evaporator absorbs heat from the air, which is then compressed by the compressor. The compressed refrigerant is then passed through the condenser, releasing the heat. The heat is then transferred to the air, and the cycle begins again. The evaporator and condenser are usually inside the home, while the compressor and metering device are outside.
Uses — Heat Pump
Heat pumps are used in heating, cooling, and refrigeration applications.
In the heating mode, a heat pump transfers heat from the cool outdoors to the warm indoors. In the cooling mode, the process is reversed, and the heat pump transfers heat from the indoors to the outdoors.
In the heating mode, a heat pump starts by drawing heat outdoors. The heat is then compressed and transferred indoors. The heat is then released into the indoor air, raising the temperature.
In the cooling mode, the heat pump reverses the process. It draws heat from the indoor air and transfers it outdoors.
How does a Heat Pump work in the winter
In winters, when the sun is at its lowest in the sky, the heat from the sun is stored in the ground. The ground has a constant temperature of around 50 to 60 degrees Fahrenheit. The water is pumped from the ground through a pipe and enters the heat pump. The water then circulates through the inside of the heat pump.
The heat pump has a fan that blows the air across the evaporator coils. The water circulating inside the heat pump carries the heat from the ground to the evaporator coils. The evaporator coils are filled with a coolant that absorbs the heat from the water. The coolant is then compressed, which increases its temperature.
The compressed coolant then enters the condenser coils located outside the heat pump. The condenser coils are filled with a coolant which passes the heat to the air through the coils. The fan blows the air across the condenser coils, carrying the heat to the room.
In winter, a heat pump moves heat from the warm outdoors into your home.
The working process of a heat pump in winter is as follows:
- A heat pump extracts heat from the air outside and transfers it inside the house.
- The heat pump compresses the refrigerant gas, which further increases its temperature.
- This hot gas is passed through the coils present inside the heat pump.
- As the heat from the gas is transferred to the coils, they start to get cold.
- This cold gas is passed through the evaporator coils inside the house.
- As the cold gas passes through the coils, the heat from the house is transferred to the gas.
- This heat is again transferred to the compressor, where the cycle repeats.
Should the heat pump constantly run in winter?
No, heat pumps do not run constantly in winter. However, they may cycle on and off more often than in other seasons.
Reasons
There are several reasons why heat pumps may cycle on and off more often in winter. Cold weather can cause the unit to work harder to maintain the desired temperature, which may cause it to cycle more frequently. Additionally, supplemental heat sources, such as electric heaters, can cause the heat pump to cycle more often.
How well do heat pumps work in winter?
Heat pumps work well in winter as long as the temperature outside is not too cold. Heat pumps work well in winter if the outside temperature is above freezing. If it is too cold, the heat pump will not be able to extract enough heat from the air and will not be able to heat the home effectively.
Uses of Heat Pump in Winters
There are a few different ways that you can use your heat pump in winter:
- You can use it to heat your home by turning on the heat pump setting on your thermostat.
- You can also use it to supplement your furnace by turning on the emergency heat setting on your thermostat.
- You can also use it to cool your home in winter by turning on the cooling setting on your thermostat.
Heat Pump Struggles in Cold Weather
When the temperature outside starts to drop, your heat pump will have to work harder to maintain a comfortable temperature in your home. This is because heat pumps move heat from one place to another, and in the winter, they have to transfer heat from the cold outdoors into your warm home.
One way to help your heat pump during the winter is to ensure that the area around your outdoor unit is clear of any debris, such as leaves, sticks, or snow. You should also make sure that your heat pump is appropriately insulated.
Another way to help your heat pump during the winter is to install a backup heating system, such as a gas furnace. If your heat pump cannot keep your home warm enough, your backup system will kick in and keep you comfortable.
How does a mini split heat pump work in cold weather?
In cold weather, a mini-split heat pump works by extracting heat from the outside air and using it to heat the inside of your home. This is possible because heat pumps operate on a refrigerant that evaporates and condenses at different temperatures, so it can absorb heat from the outside air even when it’s cold. The heat pump then transfers this heat to the indoor coils, which are used to warm the air inside your home. Mini split heat pumps are very efficient and can save you money on your heating bills.
How to Defrost your Heat Pump in the Winter?
When the weather turns cold, some heat pumps may frost over. This is because the heat pump pulls warmth from the outdoor air and, as a result, moisture condenses on the coils. While this is a regular occurrence, it can impact the efficiency of your heat pump.
Here are a few tips on how to defrost your heat pump in the winter:
-First, try raising the temperature of your thermostat. This will cause the heat pump to run less frequently, giving it more time to defrost.
-Next, check the outdoor unit to ensure nothing is blocking the coils. Leaves, dirt, and debris can impact the heat pump’s ability to function correctly.
-If the unit is still frosting over, you may need to turn off the heat pump and thaw it out manually. To do this, use a hair dryer or space heater to melt the ice. Once the ice is melted, wipe away any water and turn the heat pump back on.
With these tips in mind, you can help keep your heat pump running smoothly throughout winter!
If the ice and snow are too thick, you can use a putty knife or other sharp object to scrape the ice off the unit. Be careful not to damage the fins on the heat pump.
Once the ice and snow have melted, you can turn the power back on to the unit, and it should work correctly.
Working of Heat Pump — In Summer
In summers, when the sun is at its highest in the sky, the heat from the sun is stored in the ground. The ground has a constant temperature of around 50 to 60 degrees Fahrenheit. The water is pumped from the ground through a pipe and enters the heat pump. The water then circulates through the inside of the heat pump.
The heat pump has a fan that blows the air across the evaporator coils. The water circulating inside the heat pump carries the heat from the ground to the evaporator coils. The evaporator coils are filled with a coolant that absorbs the heat from the water. The coolant is then compressed, which increases its temperature.
The compressed coolant then enters the condenser coils located outside the heat pump. The condenser coils are filled with a coolant which passes the heat to the air passing through the coils. The fan blows the air across the condenser coils, carrying the heat to the room.
Heat pumps can reverse the process. The heat pump can reverse the summer process and be used as an air conditioner.
Heat Pump Struggles in Summer
The heat pump struggles in summers because the temperature outside is so hot. The heat pump has to work harder to cool the house down, and it can be challenging to keep the house cool. Sometimes the heat pump will shut off entirely because it can’t handle the heat, which can be very frustrating for the homeowners.
If you have a heat pump, it is essential to make sure that it is serviced regularly. This will help to ensure that it is working correctly and that it will be able to withstand the heat of summer. If your heat pump is having difficulties, you may want to consider switching to a different type of cooling system, such as an air conditioner.
How does a Heat Pump make a House Warm during Winter and Cold during Summer?
A heat pump makes a house warm during winter and cold during summer by transferring heat from the air outside to the air inside the house.
A process of refrigeration does this. The heat pump has a compressor that pumps a refrigerant through a series of coils. The coils absorb heat from the air outside and transfer it to the air inside the house.
The heat pump also has a reversing valve that reverses refrigerant flow. It allows the heat pump to transfer heat from the air inside the house to the air outside. This is how the heat pump makes a house cold during summer and warm during winter.
What is the Relation between Heat Pump Efficiency and Temperature?
The heat pump efficiency is inversely proportional to the temperature. This means that the higher the temperature, the lower the heat pump’s efficiency. Conversely, the lower the temperature, the higher the heat pump’s efficiency.
The efficiency of a heat pump varies with the temperature. When the temperature is low, the efficiency is low. When the temperature is high, the efficiency is high.
Moreover, The efficiency of a heat pump is measured by the coefficient of performance (COP). The COP is the ratio of the heat output of the heat pump to the energy input of the heat pump.
Is it safe to turn off the Heat Pump at Night?
Yes, it is safe to turn off your heat pump at night. However, you may consider leaving it on low to help maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
Some people believe it is better to leave the heat pump on at night so that the home is heated evenly and consistently, but this is not necessarily true. If the home is well-insulated, turning off the heat pump at night will not significantly affect the temperature inside the home.
Do Ecobee thermostats work with heat pumps?
As you may know, heat pumps are becoming an increasingly popular choice for home heating and cooling. Many homeowners wonder if they can use an Ecobee thermostat with their heat pump.
The answer is yes! Ecobee thermostats are compatible with all types of heat pumps. If you have a heat pump, you can use an Ecobee thermostat to control it. This means you can enjoy all the benefits of an Ecobee thermostat, such as energy savings and improved comfort.
If you’re considering purchasing an Ecobee thermostat, or if you already have one, rest assured that it will work with your heat pump. You can enjoy all the benefits of an Ecobee thermostat without any worries.
Do Honeywell thermostats work with heat pumps?
Yes, most Honeywell thermostats are compatible with heat pumps. However, it is essential to check the specific model of the thermostat to ensure compatibility. Some features, such as auxiliary or emergency heat, may not be available on all models. Consult the Honeywell website or your local heating and cooling professional for more information.
What size heat pump do you need for an average-size home?
As a general rule of thumb, you will need a 1-ton heat pump for every 1000 square feet of your home. So, for a 2500-square-foot house, you would need a 2.5-ton heat pump. However, there are other factors to consider when sizing a heat pump for your home, such as the climate you live in and your home’s insulation levels. It’s always best to consult a qualified HVAC contractor to determine the best size heat pump for your specific needs.
Heat pumps or Central Air conditioners, which one should I choose?
In the battle of heat pumps versus central air conditioners, both have their pros and cons. It depends on your specific needs as to which one is the better choice for you. Here, we look at some of the key differences between the two to help you make an informed decision.
Central air conditioners are generally more expensive to purchase and install than heat pumps. However, they are also more energy-efficient so that you may save money in the long run on your energy bills. Central ACs also tend to last longer than heat pumps – around 15 to 20 years, as opposed to 10 to 15 years for a heat pump.
Heat pumps can be used in both warm and cold climates, whereas central air conditioners are only suitable for use in hot weather. Heat pumps also have the ability to both cool and heat your home, whereas central ACs can only cool.
A central air conditioner is likely the better choice for you if you live in an area with long, hot summers and mild winters. However, a heat pump may be the better option if you live in a climate with more extreme temperatures.
Conclusion
Heat pumps are an efficient alternative to furnaces and air conditioners, providing a comfortable indoor environment while using less energy. In conclusion, heat pumps are a great way to save energy and money while providing a comfortable indoor environment.